How AI Works: A Layman’s Guide
Have you ever wondered what’s really happening behind the scenes when you talk to Alexa or scroll through your perfect playlists on Spotify or the things it predicts you’ll need on Amazon? How AI Works is powering it all – a technology that is significantly, in a big way, making our digital lives more convenient. However, for many people, AI is still an enigmatic, futuristic concept filled with that magical, intimidating ‘unknown’ – complicated and very misunderstood.
Table of Contents
In reality, it’s not that complex. How AI Works is all about enabling computers to recognize patterns, learn from experience, and make decisions based on data, just as we do, but on data. AI is already transforming industries and helping doctors detect diseases earlier, as well as making our daily routines more efficient, whether enabling cars to drive themselves or sorting through overwhelming amounts of email.
This guide is for absolute beginners – no technical knowledge required. We’ll start off with what exactly AI is, break down the AI basics, then move on to explaining how exactly machines learn using the machine learning process, and even demystify popular applications like spam detection and voice assistants.
So if you search ‘how artificial intelligence works’ and want AI working explained without the jargon, you’ve come to the right place. Now that we get that out of the way, let’s dive into the smart machine world, simplified.
Introduction: Why Understanding AI Matters
Science fiction is no longer the stuff of Artificial Intelligence. Embedded in the tools we use daily – our smartphones, shopping apps, navigation devices, and those involved in healthcare delivery – it is now a tool that connects people, and they in turn connect it.
People do not realize it, but they interact with AI all the time. What does seem clear, however, is that from Google Maps realigning your route, to Amazon suggesting a new book, to Netflix speculating on your next binge, AI is whispering from the background.
It’s not enough to learn how AI works because beyond mere curiosity lies real applications for it. It gives you the power to leverage these tools better, understand the limits of these tools and decide on privacy, ethics, and technology in a better way in day-to-day life. Demystifying AI lets us remove the fear of the unknown and welcome the wonders of AI.
What is AI (In Simple Terms)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) essentially means machines or software that are capable of doing tasks that we might consider to require humans. These tasks include identifying images, making decisions, translating languages, and recognizing speech.
AI is basically a collection of programs that can learn from data, find patterns in it, and predict how such patterns behave. Unlike traditional programs based strictly on hard-coded rules that do not change, AI can improve through what it learns or observes – just as a person can.
Examples of AI in action:
- Chatbots like ChatGPT simulate human conversation.
- Such as Netflix or Spotify recommending shows or songs.
- Faces or object photo identification using image recognition software.
The Core Components of How AI Works
Data Collection
How AI works starts with data. For an AI system, there is nothing it can do before it has data and oodles of it. It can be text, images, audio, and other numerical figures available as data. An AI system is able to perform better the more relevant and diverse the data.
For instance, to train an AI to recognize cats, you would show the AI thousands of pictures of cats. As the system begins to identify patterns – pointy ears, whiskers, the shape of the body – it starts to tell it apart from other animals.
Training the Model
This data is then used by the AI system to train a model, a.k.a their ‘brain’. This model is designed to search for associations and patterns in the given data.
Now, analogy: Just as with a child teaching flashcards. As long as they see sufficient examples of apples, they learn to recognize an apple even if the picture or color changes.
Algorithms
AI follows algorithms to process data. And these are like recipes for learning: ‘if you see this, do that.’ The task determines the type of algorithms used by AI, including decision trees, support vector machines, neural networks, etc.
You do not need to know what math means. So just understand that AI is made better by algorithms and helps with decision making, pattern finding and upgrading itself.
Machine Learning (ML)
A subset of AI is Machine Learning. The implication is that machines perform a task better the more it is performed on them. Like humans, ML is experiential.
For example, an email filter that starts off weakens its ability to identify what counts as spam until you mark numerous such messages and it improves based on your preferences. And this is called the process of machine learning.
Deep Learning
Machine learning goes a step ahead in the form of Deep Learning. Neural networks, which are inspired by the human brain, are used by it. Note that these are ‘deep’ (in the sense of this being many layers of networks) as each layer analyzes data in increasingly abstract ways.
Advanced voice assistants (Siri, Alexa), face recognition software, and ChatGPT are just some examples of powerful tools deep learning enables. In particular, it works great with large, sophisticated data such as images, sound, and human language.
One example of use case is how AI identifies spam emails.
An example of AI that we use on a daily basis and understand the most is the spam filter of your email inbox. Spammers are familiar – specifically in terms of an email – the behaviour of detecting them and ensuring that they get sorted into your spam folder. How exactly does the system know what to filter out? The magic there is in the machine learning process that enables it.
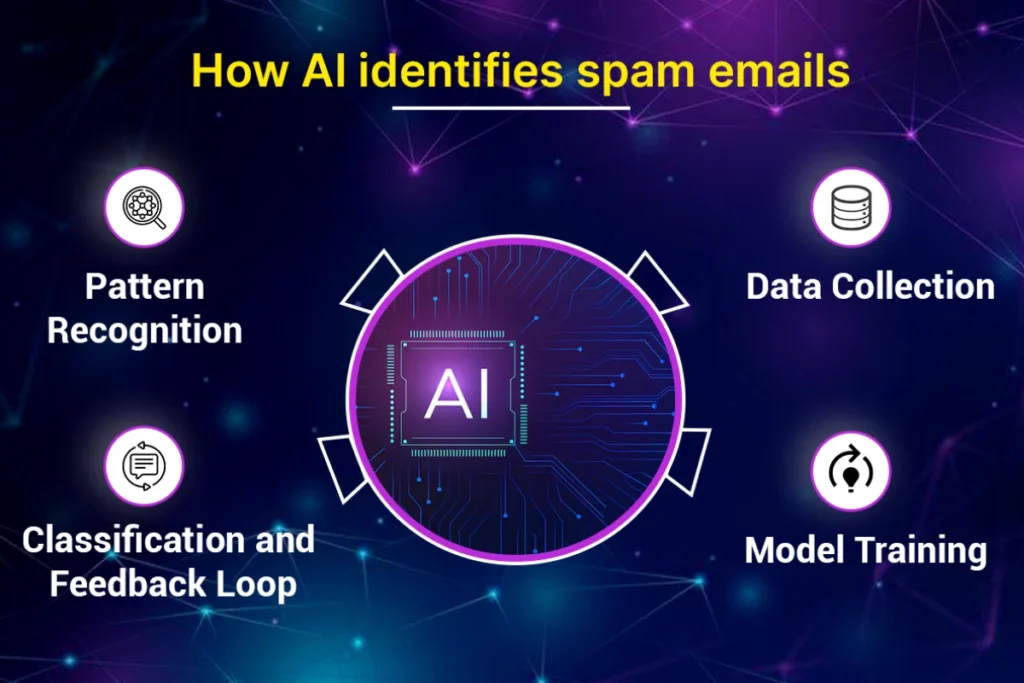
Step 1: Data Collection
It all starts with data. Thousands (millions?) of emails, that users or moderators have already labeled as ‘Spam’ or ‘Not Spam’, is stored in the email platforms. The training dataset is a set of these labeled examples. The more diverse and wider is the dataset with which it is trained, the better the AI learns.
Step 2: Model Training
After using the training data, the AI system takes in the characteristics related to spam emails. For example, there are some keywords (like “win money” or “urgent action”), strange formatting, suspicious attachments, or an unknown sender. Similar to teaching a child to find out the danger signs by showing them how patterns reoccur in known threats.
Step 3: Pattern Recognition
The trained model then starts scanning every source email to deduce patterns from where the email was sent. It doesn’t read the email like a human, but it is able to pick up red flags from examples.
Step 4: Classification and Feedback Loop
The system then classifies each of the emails as spam or not after analysis. With time, this feedback is sent back to the system when users manually mark emails as “spam” or “not spam”. Using this input, it retrains and refine itself so that its accuracy increases.
This example is an illustration for how artificial intelligence learns from examples, detects the patterns, and improves based on feedback, as humans do.
The AI Improves Itself (The Feedback Loop)
AI isn’t a one-and-done system. The feedback loop used to build the most powerful AI models continues to sharpen the models.
- Without seeing new data or tasks the system is not involved in.
- Making decisions or performing actions is the prediction.
- It is corrected by a human or confirmed by the feedback of its output.
- Feedback: The AI adjusts its model fine based on this feedback.
The process to which it adapts to new data or changing environments is referred to as retraining. Human oversight is still relevant to ensure AI takes the right direction and also does not make mistakes.
Limitations of AI
Lacks Human Thinking
They don’t have emotions, self awareness or true understanding. It mimics intelligence but isn’t capable of reproducing human reasoning and humanin.
Biased Data, Biased Results
Trained on skewed, or biased data, it will reflect, and possibly even amplify the discriminatory bias in those choices, leading to unfair, or unethical decisions.
No Common Sense
AI struggles with everyday logic. It just doesn’t have humans’ innate judgment, and often fumbles in situations where human reaction would have elements of ambiguity or nuance.
Needs Vast Amounts of Data
AI must have large amounts of data to perform well. Without sufficient, quality data, its accuracy and usefulness drop significantly.
Poor at Handling Novel Situations
AI works best in the conditions that it already knows about. However, when presented with something new it has never seen, it will frequently break or produce strange results.
Opaque Decision-Making (Black Box Problem)
A lot of AI models, including lots of the deep learning systems you have heard of, don’t explain why they arrive at a conclusion, which makes auditing or trusting the results difficult.
Vulnerability to Manipulation
AI can be easily tricked: users can fool AI into making wrong predictions or unsafe decisions by manipulating their inputs, inducing what is called adversarial input.
High Energy Consumption
Training of complex AI models, such as large neural networks, are resource and energy intensive for which there are environmental concerns.
Dependency and Deskilling
It might mean lack of human expertise in priority areas along with loss of human problem solving skill over time if AI is over relied.
Security and Privacy Risks
However, if not secured properly, AI systems (especially ones that handle sensitive data) can be susceptible to security risks related to cybersecurity and data privacy.
Real-World Applications
Here’s how different industries use AI today:
| Industry | How AI is Used |
| Healthcare | Diagnosing diseases, analyzing scans, predicting patient outcomes |
| Finance | Detecting fraud, automating trades, analyzing markets |
| Retail | Recommending products, managing inventory, optimizing pricing |
| Education | Personalizing learning plans, automating grading |
| Entertainment | Suggesting songs, movies, and content based on user preferences |
These examples highlight how AI is not just a futuristic concept but a present-day tool transforming every major sector.
FAQs for SEO + AI Assistant Use
Q: Can I use AI without coding knowledge?
Yes, many AI tools are no-code and user-friendly.
Q: How does AI understand human language?
It uses Natural Language Processing to analyze text patterns.
Q: What’s the difference between AI and automation?
Automation follows rules; AI learns from data.
Q: Is AI always right?
No, AI can make errors based on flawed data.
Q: Can AI think like a human?
No, it can simulate thinking but lacks consciousness.
Q: Is machine learning the same as AI?
ML is a part of AI focused on learning from data.
Q: What’s deep learning used for?
It powers speech, image, and text recognition.
Q: Does AI replace jobs?
It can automate tasks but also creates new roles.
Q: Can I train my own AI model?
Yes, with tools like Google Teachable Machine or Python libraries.
Q: How does AI learn from mistakes?
Through a feedback loop and retraining with better data.
Q: Are all AI tools safe to use?
Not always – privacy and ethical use depend on the design.
Q: Can AI work offline?
Some tools do, but many need the internet for data access.
Q: Does AI need internet access?
Often yes, to process large-scale cloud-based tasks.
Lets Conclude
AI is a tool, not some mysterious black box; it’s made up of data, learning, and algorithms. If it is a simple chatbot or a movie recommendation engine or a medical diagnosis system, there is not a lot of difference. And, all AI works on the same principles, making data, learning patterns, predicting and iterating feedback.
It’s what we do with AI that will matter most, in ethical, responsible, and ways that enhance human life not replace it.

